
Background
- Population—187,342,721
- Birth Rate—24.81 births per 1,000 population
- Death Rate—6.92 deaths per 1,000 population
Location
Pakistan is a soverign country in South Asia. With a population exceeding 199million people, it is the sixth most populous country. Pakistan has a 1,046-kilometre (650 mi) coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Indian to the east, Afghanistan to the west, Iran to the southwest and China in the far northeast respectively.
Provinces
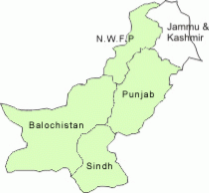
Pakistan has four provinces which have distinctly different cultures, languages, geography and climate
- Punjab is the largest province in terms of population
- Baluchistan occupies the largest land mass
- Sindh has the sea, Indus and the deserts of Thar.
- NWFP (North West Frontier Province) has the majestic mountains, including dozens of peaks over 25,000 feet.
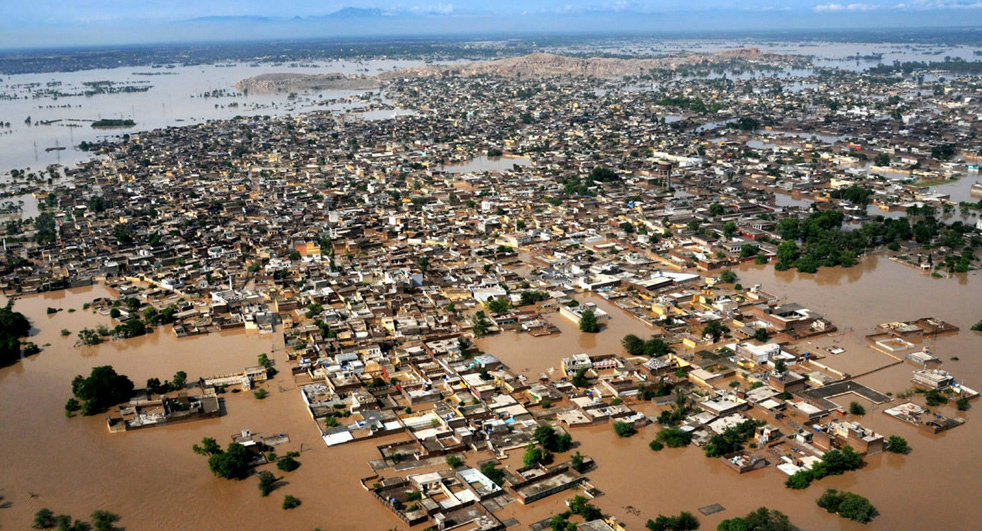
At the end of July 2010 usually heavy monsoon rains in northwest Pakistan caused rivers to flood and burst their banks.
Major Causes
- Monsoon pattern and heavy rainfall
- Climate Change
- Deforestation
- United Nations department for international disaster strategy reduction
- Taliban
The floods submerged entire provinces and left many homeless. The population on the banks of the Indus River were severely affected, the red areas show where there was the most extensive damage. The Indus River runs directly through the centre of Pakistan from the south to the north border.
- Pakistan’s climate varies from temperate to tropical with rainfall ranging from less than 10 inches to about 150 inches a year in various regions.
- Half of Pakistan’s rain falls between July and September (monsoon season) which causes intense rainfall resulting in flooding each year.
- Heavy monsoon rainfalls of more than 200 millimetres (7.9inches) were recorded during the four day wet spell from 27th July to 30th July 2010 in the provinces of Khyber, Pakhtunkhwa and Punjab based on data from the Pakistan Meteorological Department.
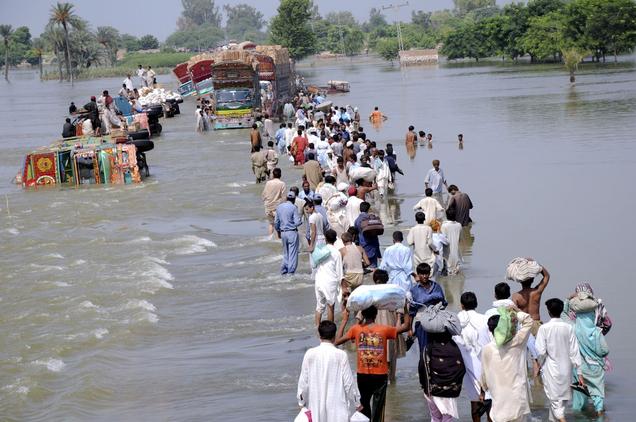

Social Effects
- 7 million people homeless and broke
- Many people living in temporary shelter
- Agricultural resources destroyed
- Food shortages were a main concern and caused food riots between the public
- A threat of social unrest : families and ethnic groups compete with each other in an event of a break down in the government
- Increased threat of diseases : cholera, malaria and malnutrition
Deforestation
Deforestation is the removal of a forest or stand of trees where the land is thereafter converted to a non forest use.
- Pakistan is known to have one of the highest rates of deforestation in the world.
- Only 5% of Pakistan is no occupied by forest due to excessive timber harvesting.
- Due to the lack of vegetation to intercept the precipitation, flooding occurs.
- Hydrological processes such as percolation, infiltration and soil saturation are hindered causing an increase in storm flow and the overflowing of surface storages which contributed to floods.
United Nations department for international strategy and The Taliban
- United Nations department for international strategy for disaster reduction focussed on water supply and food drought rather than the defences againsts the floods knowing that previous floods have had massive negative effects in Pakistan.
- The Taliban threatened to hijack foreign aid attempts in Pakistan and as a result fewer aid workers came to Pakistan to provide the required help.
NASA Statistics
- According to the statistics from NASA it was shown that there was clearly more rainfall in the July to August period of 2010 than the same period of 2009.
- From the results it can be said that the precipitation was too intense for infiltration to occur.
- As a result there was a massive increase in overland flow, which caused wide spread flooding.


